Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Random Orthogonal Measurements, Cosine Basis, ADMM¶
This example has following features:
The signal being measured is not sparse by itself.
It does have a sparse representation in discrete cosine basis.
Measurements are taken by a partial Walsh Hadamard sensing matrix with small number of orthonormal rows
The number of measurements is 8 times lower than the dimension of the signal space.
ADMM based Basis pursuit denoising is being used to solve the recovery problem.
This example is adapted from YALL1 package.
Let’s import necessary libraries
import jax.numpy as jnp
from jax import random
norm = jnp.linalg.norm
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cr.sparse import lop
from cr.sparse.cvx.adm import yall1
Setup¶
# Number of measurements
m = 1024
# Ambient dimension
n = m*8
key = random.PRNGKey(0)
keys = random.split(key, 4)
Non-sparse signal¶
xs = 100 * jnp.cumsum(random.normal(keys[0], (n,)))
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi= 100, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.plot(xs)
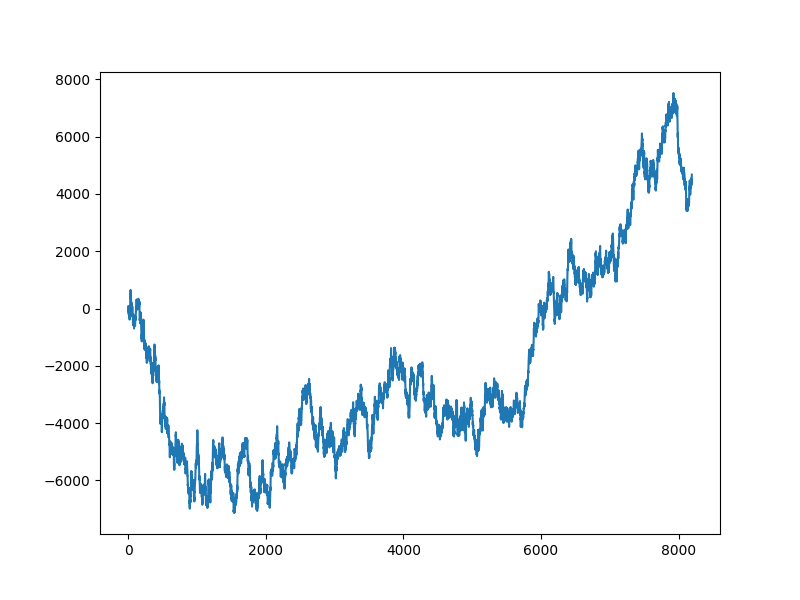
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f27aa81c8e0>]
The Sparsifying Basis¶
Psi = lop.jit(lop.cosine_basis(n))
alpha = Psi.trans(xs)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi= 100, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.plot(alpha)
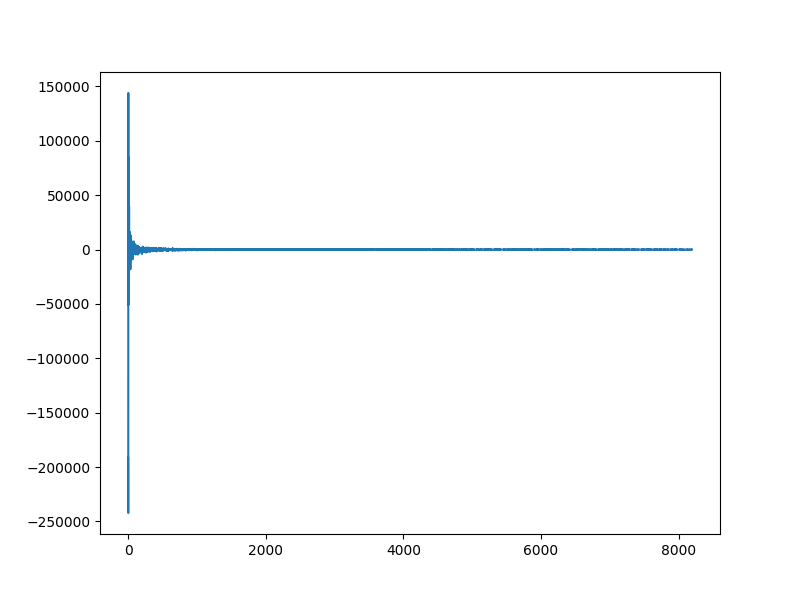
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f27ab2463d0>]
Partial Walsh Hadamard Measurements Operator¶
# indices of the measurements to be picked
p = random.permutation(keys[1], n)
picks = jnp.sort(p[:m])
# Make sure that DC component is always picked up
picks = picks.at[0].set(0)
print(f"{picks=}")
# a random permutation of input
perm = random.permutation(keys[2], n)
print(f"{perm=}")
# Walsh Hadamard Basis operator
Twh = lop.walsh_hadamard_basis(n)
# Wrap it with picks and perm
Tpwh = lop.jit(lop.partial_op(Twh, picks, perm))
picks=Array([ 0, 16, 17, ..., 8181, 8189, 8191], dtype=int64)
perm=Array([ 492, 5891, 6660, ..., 1416, 2648, 5917], dtype=int64)
Measurement process¶
# Perform exact measurement
bs = Tpwh.times(xs)
# Add some noise
sigma = 0.2
noise = sigma * random.normal(keys[3], (m,))
b = bs + noise
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi= 100, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.plot(b)
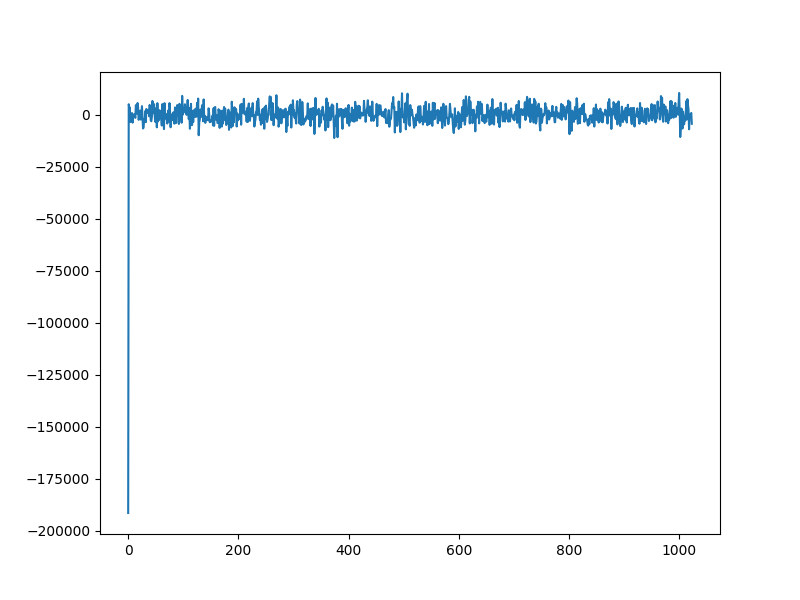
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f27ac6cf730>]
Recovery using ADMM¶
# tolerance for solution convergence
tol = 5e-4
# BPDN parameter
rho = 5e-4
# Run the solver
sol = yall1.solve(Tpwh, b, rho=rho, tolerance=tol, W=Psi)
iterations = int(sol.iterations)
#Number of iterations
print(f'{iterations=}')
# Relative error
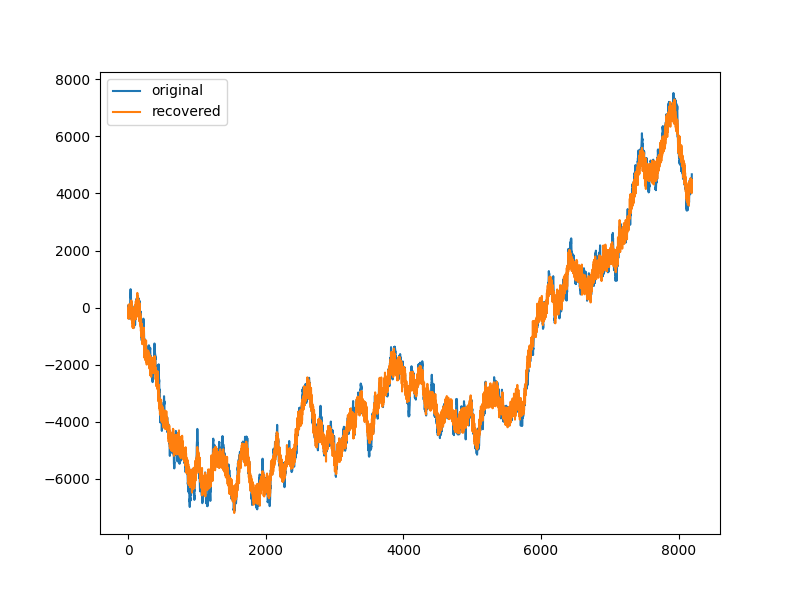
rel_error = norm(sol.x-xs)/norm(xs)
print(f'{rel_error=:.4e}')
iterations=192
rel_error=7.8711e-02
Solution¶
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi= 100, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.plot(xs, label='original')
plt.plot(sol.x, label='recovered')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f27abd23760>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.425 seconds)
